When evaluating the financial health of a company, one of the key documents to analyze is the income statement. Also known as the profit and loss statement, the income statement reveals a company’s financial performance over a specific period, narrating the story of the business’s operational activities.
Within an income statement, you’ll find all revenue and expense accounts for a set period, providing insights into the company’s profitability and expenses.
What is an Income Statement?
An income statement is a financial document that summarizes a company’s revenue, expenses, gains, and losses over a specific period, typically on a quarterly or annual basis. It provides a comprehensive overview of the company’s financial performance and helps stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and managers, understand how the business is operating.
The income statement is divided into several sections, including revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, non-operating expenses, taxes, gains, and losses. By analyzing these sections, users can gain valuable insights into a company’s profitability, efficiency, and financial health.
Why is the Income Statement Important?
The income statement is a crucial tool for both internal and external stakeholders.
Here are some reasons why it is important:
- Assessing Profitability: The income statement allows stakeholders to evaluate a company’s profitability by analyzing its revenue and expenses. It provides insights into whether the company is generating enough revenue to cover its expenses and generate a profit.
- Making Informed Decisions: Investors and creditors rely on the income statement to make informed decisions about whether to invest in or lend money to a company. By analyzing the financial performance revealed in the income statement, they can assess the company’s ability to generate returns or repay debt.
- Identifying Trends and Patterns: By comparing income statements from different periods, stakeholders can identify trends and patterns in a company’s financial performance. This helps them understand how the company is evolving and whether it is on a positive or negative trajectory.
- Evaluating Efficiency: The income statement enables stakeholders to evaluate a company’s efficiency by analyzing its cost of goods sold and operating expenses. It provides insights into how effectively the company is managing its resources and controlling its expenses.
- Meeting Regulatory Requirements: Companies are often required to produce income statements for regulatory purposes. These statements help ensure transparency and compliance with financial reporting standards.
How to Prepare an Income Statement
Preparing an income statement involves several steps.
Here’s a general guide on how to create one:
1. Gather Financial Data
Collect all the necessary financial data, including revenue figures, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, non-operating expenses, gains, and losses. Ensure that all the numbers are accurate and up-to-date.
2. Organize the Data
Organize the collected financial data into appropriate categories, such as revenue, expenses, and gains/losses. This will make it easier to create a structured income statement.
3. Calculate Gross Profit
Calculate the gross profit by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the total revenue. This figure represents the profit generated from selling products or services before deducting operating expenses.
4. Calculate Operating Expenses
Calculate the total operating expenses, including salaries, rent, utilities, and other costs associated with running the business. Subtract the operating expenses from the gross profit to determine the operating income.
5. Include Non-Operating Expenses and Gains/Losses
Add any non-operating expenses, such as interest payments or losses from investments, and gains/losses from activities outside of the company’s core operations to the operating income. This will provide a more comprehensive view of the company’s financial performance.
6. Calculate Net Income
Finally, subtract the non-operating expenses and gains/losses from the operating income to calculate the net income. The net income represents the company’s total profit or loss after accounting for all revenue, expenses, gains, and losses.
Examples

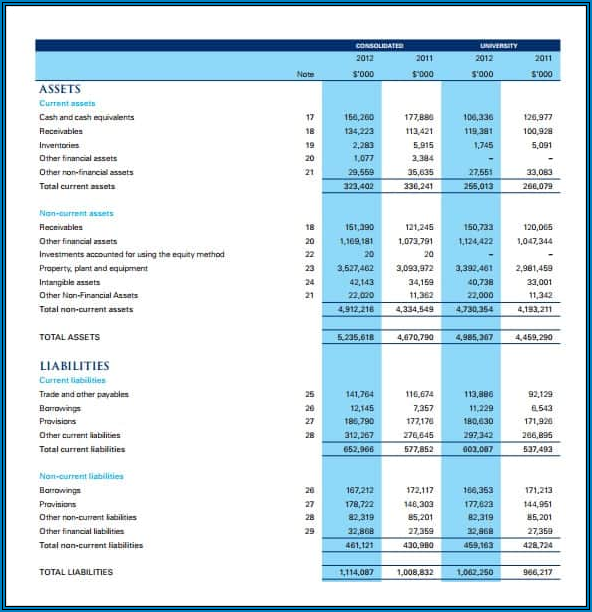


Tips for Successful Analysis of an Income Statement
When analyzing an income statement, it’s important to keep the following tips in mind:
- Compare with Previous Periods: Compare the current income statement with previous periods to identify trends and changes in the company’s financial performance.
- Consider Industry Benchmarks: Compare the company’s income statement with industry benchmarks to assess its performance relative to its peers.
- Look for Red Flags: Pay attention to any significant fluctuations or abnormalities in the income statement. These could indicate underlying issues or potential risks.
- Consider the Big Picture: Analyze the income statement in conjunction with other financial statements, such as the balance sheet and cash flow statement, to gain a holistic view of the company’s financial health.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you’re unsure about how to interpret an income statement or need assistance with financial analysis, consider consulting with a professional, such as an accountant or financial analyst.
By following these tips, stakeholders can effectively analyze an income statement and gain valuable insights into a company’s financial performance.
Conclusion
The income statement is a powerful tool for evaluating a company’s financial performance and understanding its operational activities. It provides stakeholders with crucial information about a company’s revenue, expenses, gains, and losses, enabling them to make informed decisions and assess the company’s financial health.
By analyzing the income statement and considering industry benchmarks, trends, and patterns, stakeholders can gain valuable insights and make strategic decisions to drive the success of the business.
Income Statement Template – Download
